Skeleton: The frame of a fully developed body looks like the skeleton shown in the picture here. It is composed of 206 bones, which are of different types. The skull bones are devised to give maximum protection to the brain-the atomic reactor, supercomputer and telephone exchange of our body, vertebrae spine bones give protection to the sciatic nerves-the main cable, cage of ribs give protection to the vital lungs and heart, and bones of hands and legs give movement.
This frame of bones looking like a cement-concrete structure of a building is made mainly of calcium and phosphorous and small amounts of a few mineral compounds.
Many of these bones are hollow inside where the most vital new red cells are generated. So when blood passes through these bones, red cells get mixed into it. That is why when a patient suffers from blood cancer, the bone marrow is also damaged. This in turn leads to less production of red blood cells and this vicious cycle leads to fatal consequences.
These bones contain inorganic chemicals like calcium, phosphorous, iron, etc. which make these bones hard; and also organic chemicals which produce red blood cells. These bones complete their growth before 20 to 23 years and so after this age height does not increase.
Muscles : (They are like the brick work with plaster inside.) The bones and their joints are covered with muscles. There is a network of muscles in the body and it weighs more than 50 % of the body’s weight. Muscles are fibrous tissues that produce movement in the body. They are secured to the bones by cords called the tendons. You can easily see the tendons at work by moving your hand and noticing where these cords move underneath the skin. The bones of moving joints are secured together by fibres called ligaments and soft pads of cartilage.
They act as cushions where the bones move over each other. Muscles work in groups, so in order to move a limb certain muscles contract and pull on the tendons, thus moving the bone, while compensating muscles stretch to keep the movement steady. Muscles are mainly of two types : voluntary and involuntary. The voluntary muscles work as per our will and are mainly concerned with movements of limbs. Involuntary muscles are found in the blood vessels, in the iris of the eye, trachea, food pipe, heart, diaphragm, etc. in the body.
In short, the voluntary muscles carry out controlled movements, while the involuntary muscles with their slow rhythmic movements are concerned with automatic functions such as breathing, working of the heart, food digestion, etc. These voluntary muscles can be developed and made strong by exercises. Heavy exercises can build up these muscles, but in that case, these muscles lose their suppleness. But yogic exercises, walking, swimming, etc. give suppleness and tone to these muscles.
If there is undue pressure on these joints and ligaments, like when an ankle gets twisted while walking or when there is a fall, there is a sprain in these joints and ligaments. In such cases, the pain subsides with rest, and with the application of hot/cold packs. The affected part should be covered with elastic bands.
Skin : It is like an outside plaster of a building. The framework of bones, skeleton, muscles and fats, are covered with skin which has seven layers, but only 1.5 millimeter thick and it is porous. It has its outer layer with sensory glands which impart to us its sense of touch; the real skin and respiration glands. They are connected by both types of afferent and efferent nerves which take sensations of coldness, heat, softness, hardness, pressure, etc. to the brain and bring back the orders from the brain.
The skin protects the muscles and fats of the body. It also prevents bacteria from entering the body. Moreover, many toxins are thrown out of the body through the skin, thus serving as a blood purifier. It helps the removal of certain salts of the body through perspiration.
It controls the temperature of the body and prevents cold from entering the body in cold season and throws out heat in the hot season through perspiration. The hair on the skin also assist in controlling the temperature of the body.Surprisingly, even though the skin is thin and delicate, it is very strong and elastic.
Digestive System : (Nutritive material manufacturing wonderful chemical plant of the body.) For the working of the body and nutrition, the organs, muscles and other tissues require blood. Pure blood is formed from the food and drink we take and digest. Our digestive system consists of mouth, buccal cavity, oesophagus, stomach, intestines (small and big), ileocaecal valve, pancreas, liver, etc.
Mouth : This is the opening of the system through which food and drink enter the system.
Buccal Cavity : This is the hollow space behind the teeth where the food is chewed with the help of teeth. Saliva is secreted from the salivary glands. This mixes with the food and helps in the digestion of sugars. Proper chewing of food at least 12-15 times is most necessary. Talks should be avoided while eating-instead, light music could be played.
Oesophagus (Gullet) : Normally this remains closed, but when food is forced into it, it directs the food downwards automatically with special movement called peristalsis. This food is pushed into the stomach.
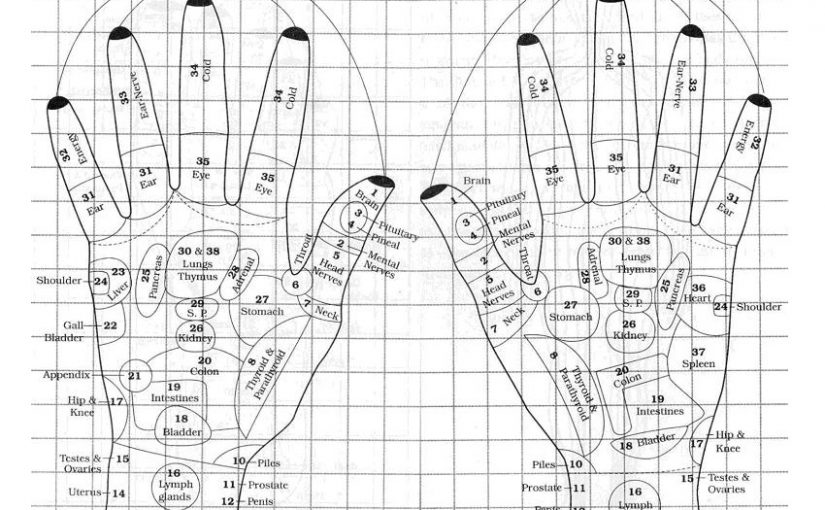
Stomach (Mixer) (Point No. 27) : When the food enters the stomach, it secretes digestive juices like pepsin and renin which help in the digestion of proteins. The churning of the food and mixing of the digestive juices goes on for about 4 hours. Then the semidigested and liquified food finds its way into the duodenum through the pyloric valve.
Digestive Organs
In order to enable the stomach to function efficiently, one should not overload it with food more than necessary, so that it can expand and contract properly. Moreover, one should make a habit of not eating between two meals and to give 9 to 10 hours of rest to the stomach at night. “To live long and healthy eat only when you are very hungry.” said Sir M. Visvesvarayya, eminent engineer, educationist and Bharat Ratna award winner, who lived for 101 years.
Small Intestine (Point No. 19) : It is about twenty-three feet i.e. seven metres long tube. The anterior (about nine inch) part is called duodenum. The bile juice created by the liver (Point No. 23) and stored in the gall bladder (Point No. 22) and pancreatic juice are poured into the duodenum where it mixes with the food. Jejunum, the middle part of the small intestine is about seven to eight feet long. The last part is called Ilium and is about fifteen to sixteen feet long. Digestive juices secreted here get mixed with the food and help in the digestion.
The bile is alkaline in nature. It neutralizes and renders the semi-digested acidic food coming from the stomach, alkaline; so as to allow the pancreatic enzymes to act. Bile juice also helps the fat to be emulified and made soluble for easy digestion. Most of the food is digested in the small intestine and broken down into simpler products like amino acids, monosaccharides like glucose, monoglycerides and free fatty acids which are absorbed in the small intestine. These absorbed juices are turned into blood by spleen.
The unabsorbed residue goes into the large intestines through ileocaecal valve (Point No. 21). It is the world’s best sewage system. The necessary amount of water and certain salts are absorbed here. This large intestine consists of the caecum (with the appendix) and the colon which ends into rectum. Depending on their position, parts of the colon are named as ascending colon, traverse colon, descending colon and the sigmoid colon. Inflammation of the colon is known as Colitis. It may be noted that if the food is properly digested and liquid intake is sufficient, the stool is properly formed-soft and nearly odourless.
Appendix (Point No. 21) : It is a worm shaped tube arising from the caecum. It is about four inches long and has no special function, but it often gets inflamed due to accumulation of decaying faecal matter or worms lodged inside it. It causes severe pain and vomitting. This can be corrected with Acupressure treatment [(Change in diet-(say (jreen juices and fruit juices), and surgery can be avoided.)]
Pancreas (Point No. 25) : It is a digestive-an exocrine gland; however as it produces insulin, it is also called an endocrine gland. Its digestive juices help in digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It creates insulin which assists the body in maintaining of sugar level of blood. It is likely that whenever energy is required by the body as demanded by adrenal gland to do some action quickly; the insulin producing parts of pancreas slows down its process and allows more sugar / glucose = energy to go to the necessary parts of the body.
Now if this process is repeatedly continued due to excitement over functioning of adrenal gland the pancreas slows down its process of creating enough insulin and over a period of few years becomes sluggish; so the control of sugar/glucose level in the body slows down and a stage is reached where diabetes sets in.
Therefore, for those people who are not overweight but have diabetes, should control adrenal and cure excess excitedness and worries and activate the pancreas to cure the diabetes. Thus, if adequate insulin is not produced by the pancreas, the result is diabetes. However, its overworking leads to more consumption of sugar/glucose and leads to low B.P., migraine, headache, etc.
Liver (Point No. 23) : Our body has a reactor-producing energy and heat. Our body requires a cooling system to control this heat. This is Liver. Its working can be compared with the working of the radiator of a car. It produces bile juice which is stored in gall bladder (Point No. 22) and from there, whenever necessary, it is poured into the duodenum-part of small intestine and turns the acidic semi-liquid food into alkaline.
Now, if the liver does not function properly and produce sufficient bile and if there is no free flow of this stored bile from gall bladder into the small intestine, acidity in the digestive system increases. This in turn leads to excess heat in the body. On the one hand more acidity in the digestive system leads to gases, burning sensation in the stomach and in gullet, weakening the gums and the teeth, and later on leading to ulcer in the intestines and the mouth.
On the other hand, production of excess heat in the body becomes the root cause of cold due to heat; disturbs the functioning of the eyes, one of the root causes and it is also that necessitates the use of spectacles, also it makes the semen, ova thinner-leading to early ejaculation and discharge in sleep for men and also to Leukorrhea in women; it also leads to problems of skin, falling of hair and is one of the main causes of Jaundice. Such a vicious cycle also leads to short-temperedness.
The proper functioning of liver is most vital and hence it is the biggest gland in the body. Moreover, it stores fats, minerals and vitamins. It converts sugar into Glycogen and vice-versa and stores it. Moreover, liver removes toxins and destroys unwanted by-products. Further, it converts cholesterol into bile.
Thus, it will be observed that as proper functioning of many organs of the body depends upon proper functioning of the liver. The quality of life is rightly said to depend upon the liver. However, its functioning is disturbed by excess heat inside the body.
Such an excess heat in the body is created by less functioning of hver and also due to cobalt and Infra-Red rays, heat producing anti-biotic drugs, drugs which disturb the proper functioning of liver and also due to the exposure to outside heat. In all these cases, it is utmost necessary to take treatment (shown later on in this book) to reduce excess heat in the body.
Working of liver is controlled by adrenal gland (Point No. 28).